On April 2, 2016, Proofpoint researchers discovered that the Magnitude exploit kit (EK) [1] was successfully exploiting Adobe Flash version 20.0.0.306. Because the Magnitude EK in question did not direct any exploits to Flash 21.0.0.182, we initially suspected that the exploit was for CVE-2016-1001 as in Angler [2], the combination exploit "CVE-2016-0998/CVE-2016-0984" [3], or CVE-2016-1010.
In the course of our investigation, we shared our findings with fellow researchers in the security community in order to accelerate identification of the exploit. A colleague at FireEye determined [4] that the exploited vulnerability was unknown. Adobe was promptly notified of the issue, and they verified that although a mitigation integrated in 21.0.0.182 appeared to cause the exploit to fail, it was a previously unreported vulnerability and assigned it CVE-2016-1019. An emergency patch for the vulnerability was released on April 7 [5].
Despite the fact that this new exploit could potentially work on any version of Adobe Flash, including a fully patched instance of Flash, the threat actors implemented it in a manner that only targeted older versions of Flash. In other words, equipped with a weapon that could pierce even the latest armor, they only used it against old armor, and in doing so exposed to security researchers a previously unreported vulnerability. We refer to this type of faulty implementation as a “degraded” mode, and it is something that we have observed in the past with CVE-2014-8439 [6] [7] and CVE-2015-0310 [8] in Angler. While there will be a period of time when systems are not yet patched for CVE-2016-1019 and thus vulnerable to new exploits, “degraded” implementations of potential zero-day exploits offer security researchers and vendors a valuable opportunity to identify and mitigate previously unknown vulnerabilities.
Let’s look at this ‘degraded’ implementation of CVE-2016-1019 in action:
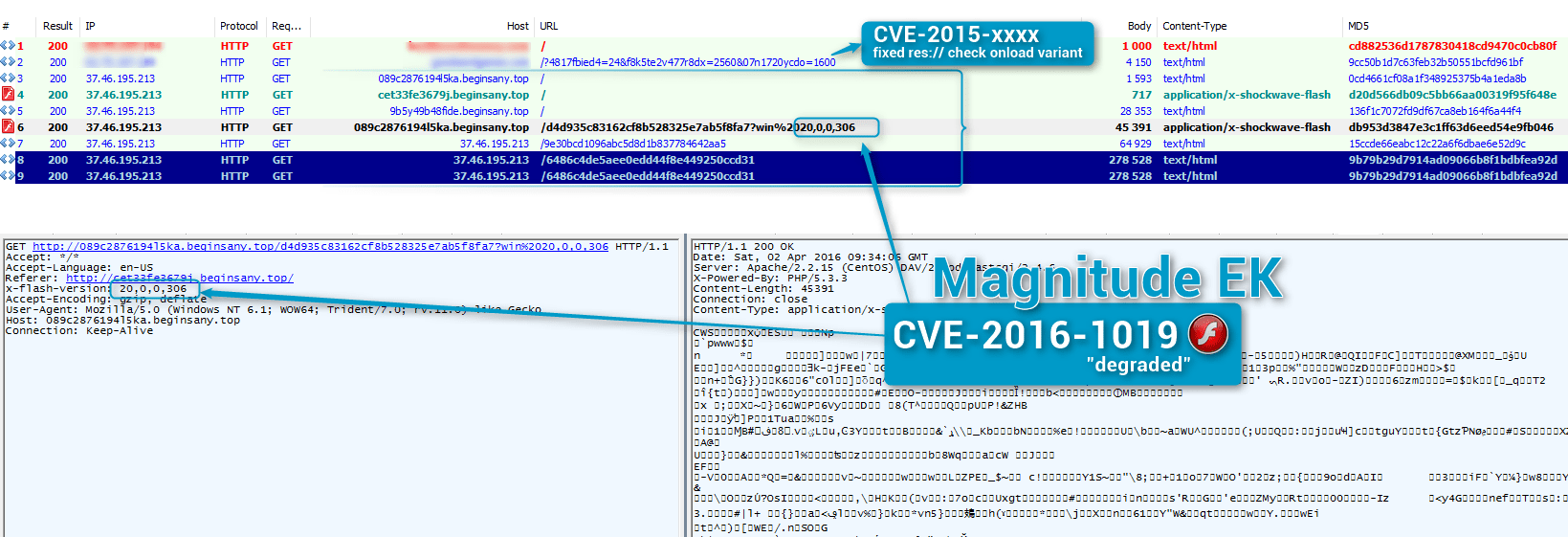
Figure 1: 2016-04-02 Magnitude exploiting CVE-2016-1019 in “degraded” mode to spread Cerber ransomware
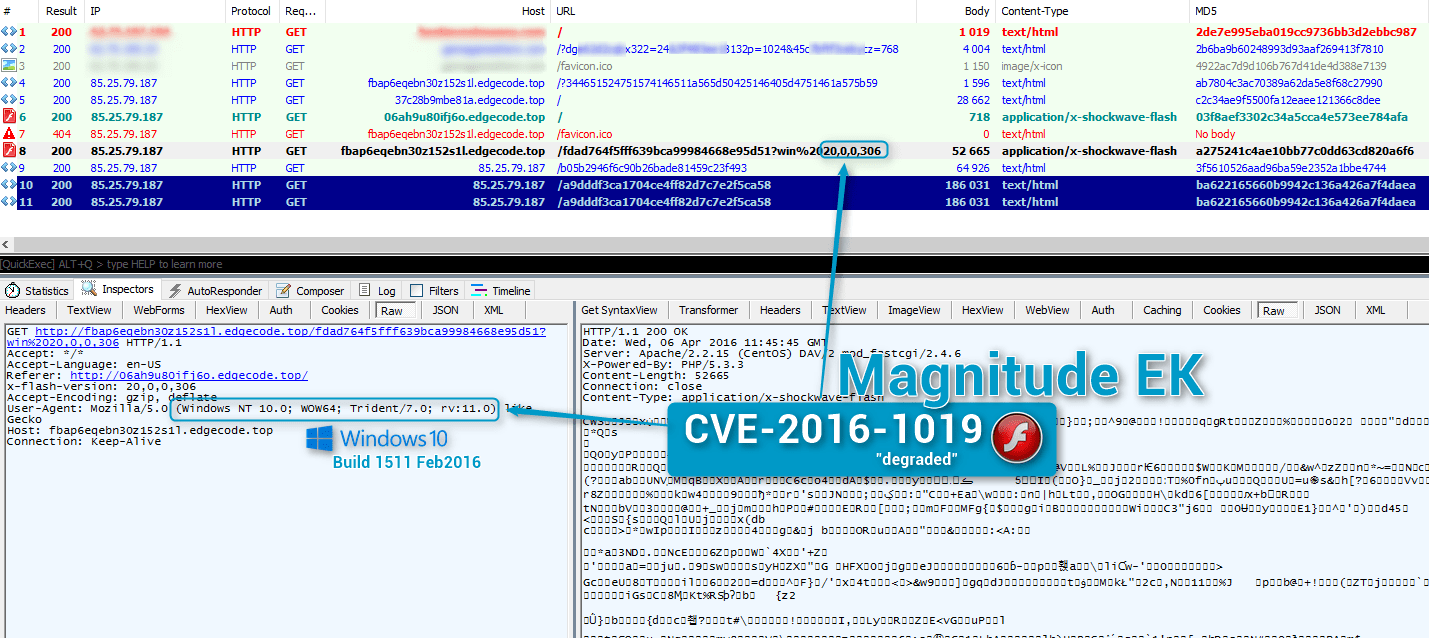
Figure 2 : 2016-04-06 Magnitude exploiting CVE-2016-1019 in “degraded” mode on Windows 10 build 1511 (Feb 2016) with Flash 20.0.0.306
Payloads
In recent months, Magnitude seems to be used by only one actor, who was spreading Cryptowall crypt1001 until the middle of March 2016. The actor then switched to distributing Teslacrypt ID=39, and since the end of March has switched to distributing Cerber [9].
We looked back at a Nuclear Pack Flash exploit move we spotted on March 31, 2016. As we did not witness a new Flash version being exploited, we did not investigate before but the embedded exploit is the same as that discovered in Magnitude (CVE-2016-1019) according to Anton Ivanov (Kaspersky), and researchers at ESET and FireEye.
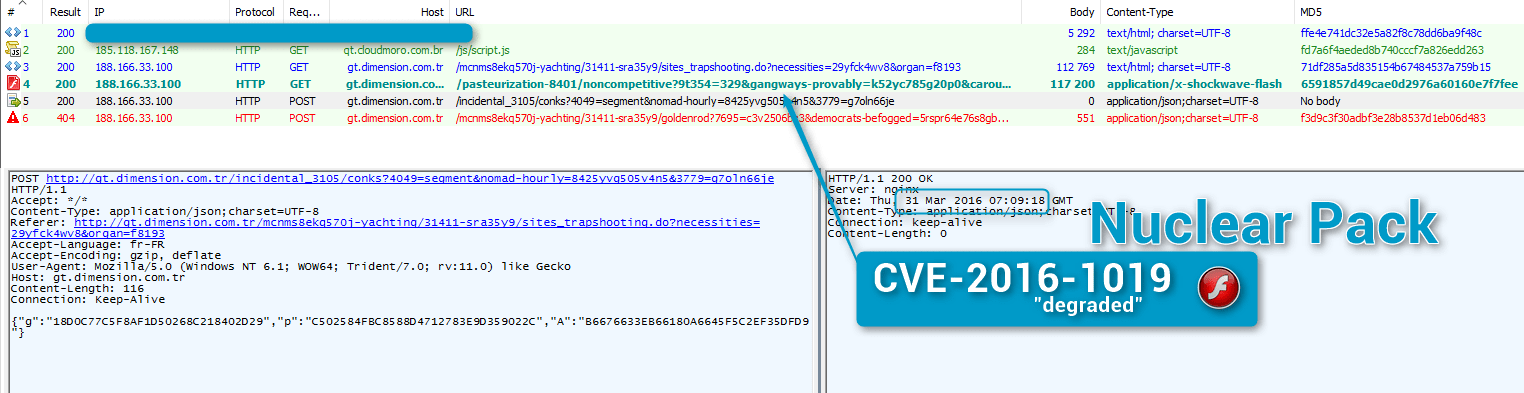
Figure 3: 2016-03-31 Nuclear Pack not exploiting Flash 20.0.0.306 despite integrating CVE-2016-1019 code (that is, not dropping the expected Locky or Necurs from the actor behind this infection chain [10])

Figure 4: Intriguing CVE-2016-1001 string spotted by Denis O'Brien (Malwageddon), the 2016-04-05 in Nuclear Pack exploit
Summarizing the main findings of this analysis:
- Magnitude EK was found to be exploiting a previously unreported vulnerability in Adobe Flash, now assigned CVE-2016-1019.
- Due to a faulty implementation of the exploit, it was not targeting the latest, fully patched versions of Adobe Flash in a way that could result in infection.
- The exploit has been in the wild since at least March 31, 2016.
- The exploit was observed spreading the Cerber and Locky ransomware, among others.
- There is evidence that Nuclear Pack was also equipped with code to exploit CVE-2016-1019 but did not run it against fully patched systems.
- Adobe has issued an emergency patch and advisory (APSA16-01) for this vulnerability.
If Adobe Flash Player is required in your environment, we advise an immediate installation of the update.
References
[1] - http://malware.dontneedcoffee.com/2013/10/Magnitude.html
[2] - http://malware.dontneedcoffee.com/2016/03/flash-up-to-2000306.html
[3] - https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.fr/2016/03/life-after-isolated-heap.html
[4] - https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2016/04/cve-2016-1019_a_new.html
[5] - https://helpx.adobe.com/security/products/flash-player/apsa16-01.html
[6] - http://malware.dontneedcoffee.com/2014/10/cve-2014-0569.html
[7] - https://www.f-secure.com/weblog/archives/00002768.html
[8] - http://malware.dontneedcoffee.com/2015/01/cve-2014-9162-flash-1500242-and-below.html
[9] - https://blog.malwarebytes.org/intelligence/2016/03/cerber-ransomware-new-but-mature/
Indicators of Compromise (IOC’s)
| md5 | sha256 | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| b3ce4f4e70a8e750205f1452d4820d3397a9d1feb495e7514602554918b582d5 | Zip with most of the content mentioned below | |
| 6591857d49cae0d2976a60160e7f7fee | 301f163644a525155d5e8fe643b07dceac19014620a362d6db4dded65d9cad90 | CVE-2016-1019 Nuclear Pack 2016-03-31 |
| db953d3847e3c1ff63d6eed54e9fb046 | 0a664526d00493d711ee93662a693eb724ffece3cd68c85df75e1b6757febde5 |
CVE-2016-1019 Magnitude 2016-04-02 |
| 5a59b3fa1dbb5849cec4cc84d386b5d3 | 7f31af42154cfc3609ca8e7b185a43c9a1d9704e6faf56b2928e32d5190592f0 |
CVE-2016-1019 Magnitude 2016-04-03 |
| da9fa0250214891ecf0539d04fdbfa3f | 32557944d18cc3b3d80de1597b74dc505297751d9440e4a9d8064cf329dd7141 |
CVE-2016-1019 Magnitude 2016-04-04 |
| 575e7b41d4dcb0e181f289d82f6f7c79 | f7c5a855dd17ac50c8de364117a96ab711daa5c723d471c19a92bf5b9e5bd2ae |
CVE-2016-1019 Magnitude 2016-04-05 |
| 9b79b29d7914ad09066b8f1bdbfea92d | 9d92fb315830ba69162bb7c39c45b219cb8399dd4e2ca00a1e21a5457f92fb3c | Cerber |
| 8bcafee60ef0101891494f16348a3e2d | 57032a0c84b6ed24fca740f9ff0f4cb183c78eeb87e0f7f386849f0b92b49816 | Cerber |
| ac193f297233d7efe1236da311affad3 | ea71c1eec6e2f2f14a643f90fd4efcec10a0f6aae43950171f7b0384572a74df | Cerber |
| 6a8ff8f206511a1d95c46741a2e00894 | 7229ab31adc3184f399be4f453d5a9d61f3c7e1347d5464d4de63a56d4762c7f | Cerber |
| Domain/IP | Comment |
|---|---|
| 37.46.195.0/24 | IP Range hosting some Magnitude proxies |
| 188.138.71.0/24 | IP Range hosting some Magnitude proxies |
| 85.25.79.0/24 | IP Range hosting some Magnitude proxies |
| 62.75.197.0/24 | IP Range hosting proxies redirecting (mostly but not exclusively) to Magnitude |
| futuremygames[.]com | Redirector to EK |
| my-playcity[.]com | Redirector to EK |
| goodsandgames[.]com | Redirector to EK |
| playenjoymy[.]com | Redirector to EK |
| nextdaysgame[.]com | Redirector to EK |
| orealore[.]com | Redirector to EK |
Select ET Signatures that would fire on such traffic:
2816837 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Evil Redirector Leading to EK Mar 30 M3
2816832 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Evil Redirector Leading to EK Mar 30 M2
2816800 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Magnitude EK Landing Mar 29 2016
2816329 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Possible Magnitude EK Flash Exploit URI Struct Feb 19 2016
2816339 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Magnitude EK Flash Payload Feb 19 2016
7016687 || ET LUAJIT WEB_CLIENT Suspicious Adobe Flash file (Compressed)
2012088 || ET SHELLCODE Possible Call with No Offset TCP Shellcode
2000419 || ET POLICY PE EXE or DLL Windows file download
2009897 || ET MALWARE Possible Windows executable sent when remote host claims to send html content
2016538 || ET INFO Executable Retrieved With Minimal HTTP Headers - Potential Second Stage Download
2021076 || ET INFO SUSPICIOUS Dotted Quad Host MZ Response
2816505 || ETPRO TROJAN Cerber Ransomware UDP Scanning
2816506 || ETPRO TROJAN Possible Cerber Ransomware IP Check
2816763 || ETPRO TROJAN Ransomware/Cerber Checkin 2
2816764 || ETPRO TROJAN Ransomware/Cerber Checkin Error ICMP Response
2816772 || ETPRO TROJAN Ransomware/Cerber Onion Domain Lookup
2814492 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Nuclear EK Landing Oct 20 2015 M1
2814493 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Nuclear EK Landing Oct 20 2015 M2
2814389 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS possible Nuclear EK DHE traffic client to server
2815818 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Possible Nuclear EK Flash URI Struct Jan 14 M2
2815810 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS Possible Nuclear EK Payload VarLen XOR (Nulls)

