Email-based attacks are the number one attack vector for cybercriminals. These attacks do not always require a high level of technical sophistication to carry out. And because the human factor is involved, there is almost no doubt they will endure as a favored tactic.
One way bad actors can greatly increase their chances of a successful attack is when they can make a recipient believe that they are interacting with a person or a brand that they know or trust. “Email spoofing” plays a critical role in helping to create this illusion. In this blog post, we’ll explain how email spoofing works, why it causes havoc, and how DMARC can protect your business.
How bad actors use email spoofing
When an attacker uses email spoofing, they are forging the sending address so that the message appears to come from a legitimate company, institution or person. Bad actors use spoofed domains to initiate attacks like phishing, malware and ransomware, and business email compromise (BEC). Here is a closer look at these strategies.
- Phishing attacks. A bad actor sends a spoofed email, pretending to be from a legitimate source like a bank, government agency or a known company. Their aim is to get the recipient to reveal sensitive information, like login credentials, financial information or personal data.
- Malware. Spoofed email can contain malicious attachments or links. When a user clicks on them, they trigger the delivery of viruses, ransomware, spyware or other types of malicious software. These tools help attackers to steal data, disrupt operations or take control of systems.
- Business email compromise (BEC). Many threat actors use spoofed email to trick employees, partners or customers into transferring money or giving up sensitive information. It can be a lucrative endeavor. Consider a recent report from the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center, which notes that losses from BEC attacks in 2023 alone were about $2.9 billion.
Negative effects of email spoofing
When an attacker spoofs legitimate domains and uses them in attacks, the negative repercussions for companies can be significant. Imagine if your best customer believed that they were communicating with you, but instead, they were interacting with an attacker and suffered a significant financial loss. Unfortunately, these scenarios play out daily. And they can lead to the following issues, among others.
The loss of trust
If attackers succeed in their efforts to spoof a company’s domain and use it to send phishing emails or other malicious communications, recipients may lose trust in that business. When users receive spoofed emails that appear to come from a brand they trust, they may become wary of future communications from that brand. They will lose confidence in the company’s ability to protect their information.
Damage to brand image
As noted earlier, a spoofed domain can tarnish a company’s brand image and reputation. If recipients fall victim to phishing or other scams that involve spoofed domains, they may associate the business or brand with fraudulent or unethical behavior.
Financial losses
Spoofed domain attacks can result in financial losses for companies in two main ways.
- Direct financial losses. Such losses can occur when attackers use spoofed domains to carry out fraudulent activities like the theft of sensitive data or unauthorized transactions.
- Indirect financial losses. These losses take the form of costs associated with attack mitigation. They can stem from incident investigation, the implementation of security improvements, and efforts designed to help repair the company’s damaged reputation.
Customer dissatisfaction
Customers who are victims of spoofed domain attacks may experience frustration and anger. They may be motivated to write negative reviews of a company or issue complaints. Certainly, their level of customer satisfaction will take a hit. Over time, repeated incidents of spoofing attacks can erode customer trust and loyalty. It can lead to the loss of customers, new business opportunities and revenue for a company.
Implement DMARC to help prevent spoofing
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is a powerful tool to help prevent email spoofing. This email security protocol builds on existing email authentication mechanisms and provides instructions based on the authentication results. Those mechanisms include:
- SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, which allows domain owners to specify the IP addresses authorized to send email on behalf of their domain
- DKIM, or DomainKeys Identified Mail, which adds a digital signature to each outgoing email
With DMARC, domain owners can specify policies to handle emails that fail authentication checks. These policies include “none,” “quarantine” and “reject.” In short, if an email fails authentication, a set policy dictates whether it can be delivered as usual, marked as spam or rejected outright.
DMARC provides a reporting mechanism for domain owners to receive feedback on how receiving mail servers handle their emails. This includes information about email authentication results, which helps the domain owners identify potential spoofing attempts or misconfigurations.
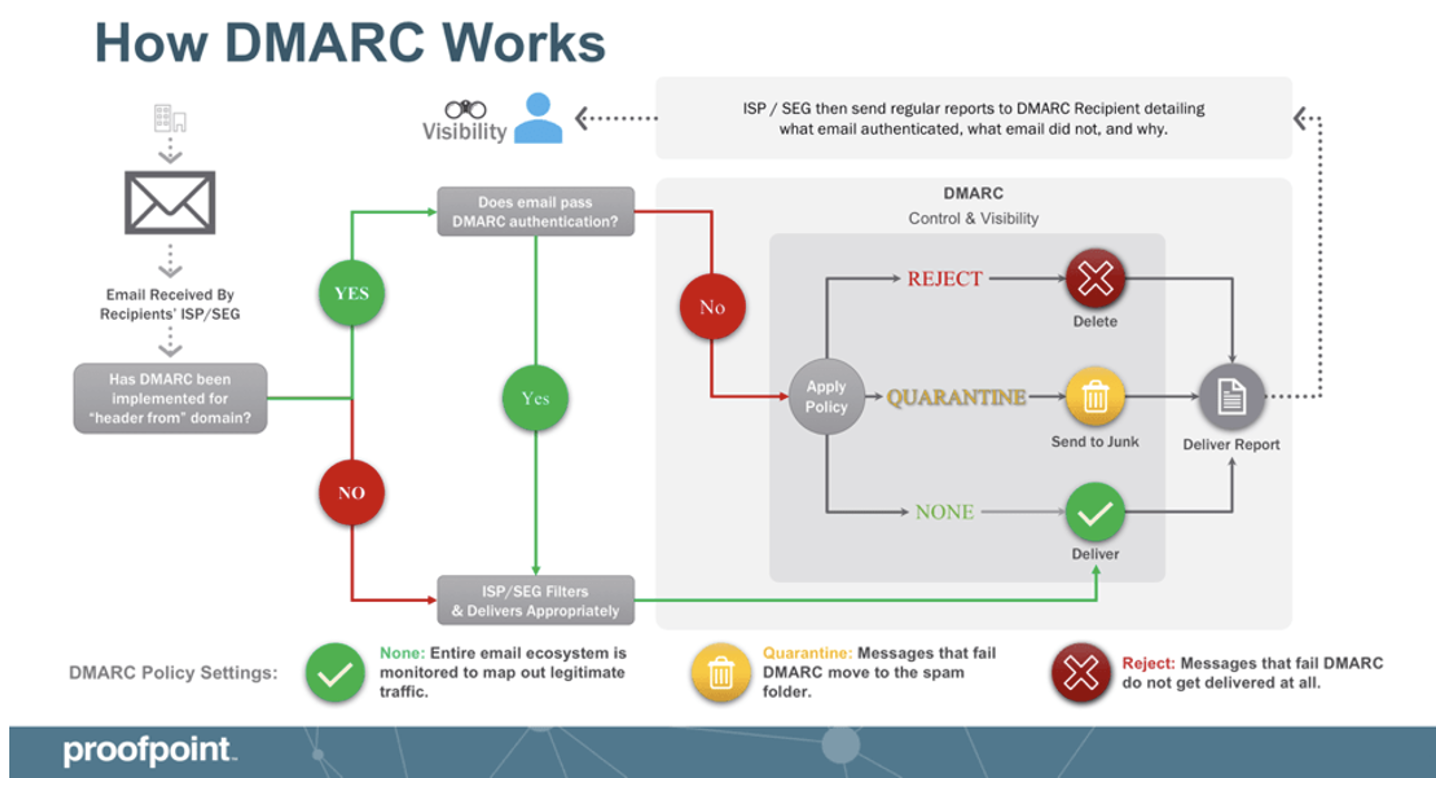
An overview of how DMARC works.
Benefits of DMARC
DMARC plays a crucial role in the prevention of email spoofing. It helps reduce an attacker’s ability to launch a successful email-based cyberattack that relies on impersonation to prey on users’ trust. When a domain owner implements DMARC, they can expect to see these benefits, among others:
- Improved spoofing prevention. DMARC helps to prevent malicious actors from impersonating legitimate domains. It does this through the enforcement of email authentication checks.
- Better brand protection. Using DMARC to prevent the unauthorized use of their domains in phishing attacks helps businesses to protect their brand reputation and maintain trust with customers.
- Access to actionable insights. DMARC has reporting features that provide valuable insights into how email traffic is handled. Domain owners can, in turn, use that information to identify and mitigate security threats more effectively.
How Proofpoint can help
It’s critical for companies to understand that reaching p=reject is not the end when it comes to DMARC. They should view DMARC as a journey, not a destination. And to maximize the effectiveness of DMARC and avoid potential issues with legitimate email delivery, they must configure and monitor DMARC policies properly.
If your business has not yet implemented DMARC, now is the time to start. Proofpoint can help. We are an industry leader in email security. We have more Fortune 1000 customers using our technology for email authentication than the next five closest competitors combined.
Proofpoint offers a holistic solution to help address impersonation threats, including email spoofing. Our highly skilled consultants have the knowledge and expertise to guide you through your DMARC implementation journey. To learn more, contact us today.

